
Interplay of folded domains and the disordered low-complexity domain in mediating hnRNPA1 phase separation | bioRxiv

Tuning levels of low-complexity domain interactions to modulate endogenous oncogenic transcription - ScienceDirect

Low-complexity domains adhere by reversible amyloid-like interactions between kinked β-sheets | bioRxiv

Imaging dynamic and selective low-complexity domain interactions that control gene transcription | Science

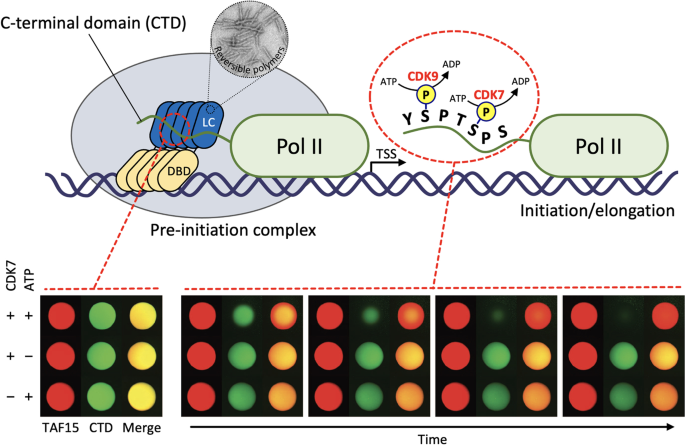
Phosphorylation-Regulated Binding of RNA Polymerase II to Fibrous Polymers of Low-Complexity Domains: Cell

The low-complexity domain of the FUS RNA binding protein self-assembles via the mutually exclusive use of two distinct cross-β cores | PNAS

Sequence of HasCL10contig2, a repetitive low complexity domain (RLCD)... | Download Scientific Diagram

Imaging dynamic and selective low-complexity domain interactions that control gene transcription | Science

ALS Mutations Disrupt Phase Separation Mediated by α-Helical Structure in the TDP-43 Low-Complexity C-Terminal Domain - ScienceDirect

Sequence Determines the Switch in the Fibril Forming Regions in the Low- Complexity FUS Protein and Its Variants | The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters
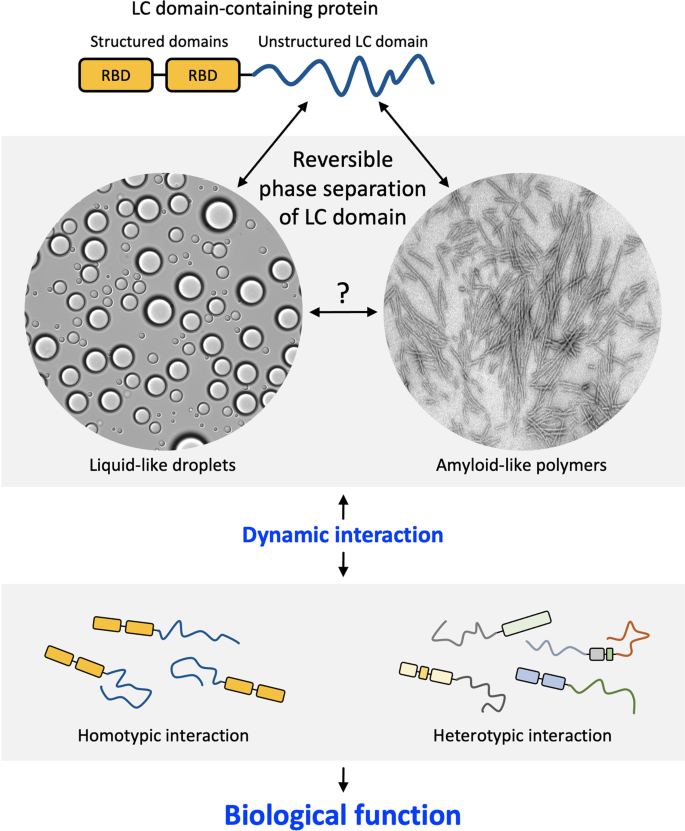
Phase separation of low-complexity domains in cellular function and disease | Experimental & Molecular Medicine
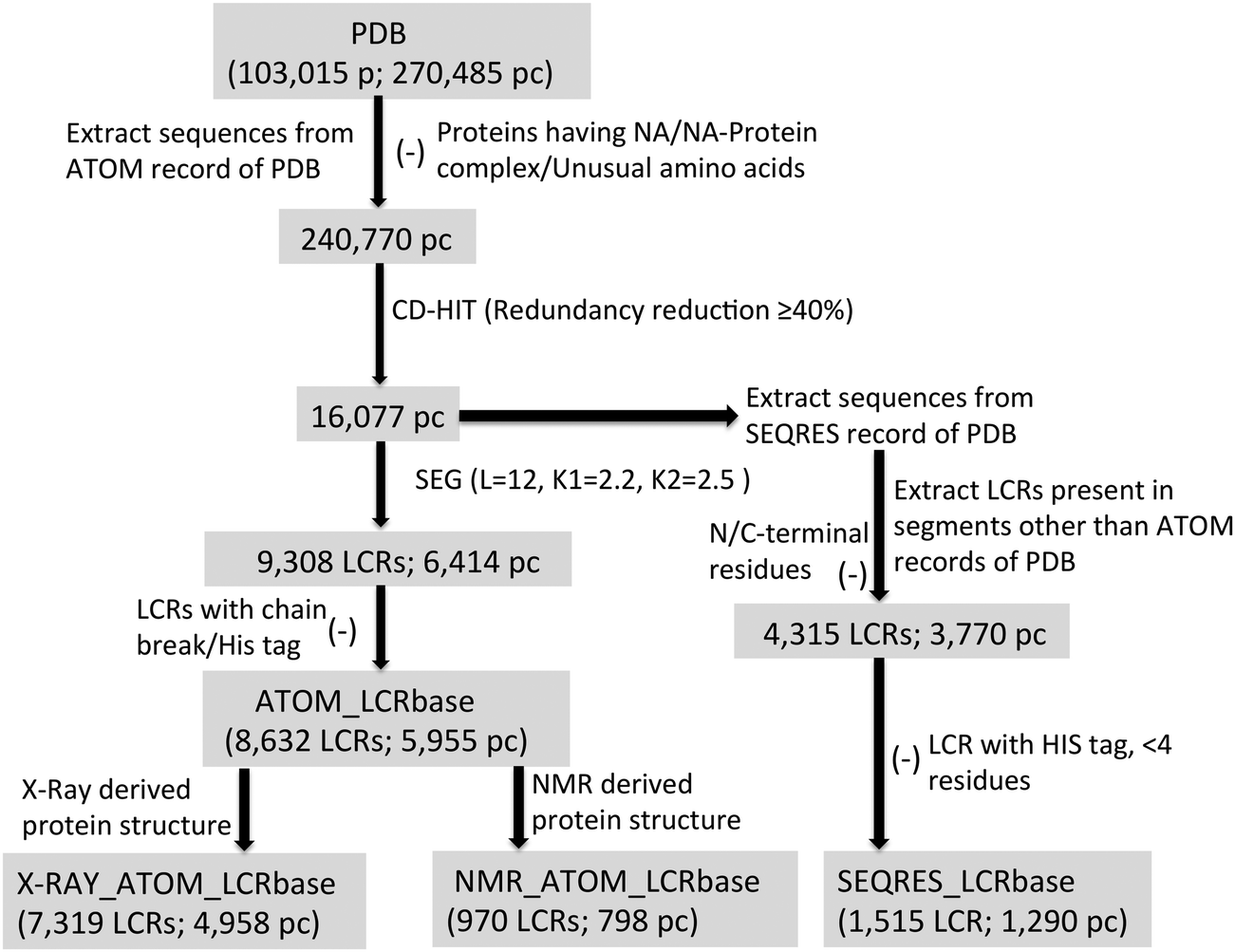
Low complexity and disordered regions of proteins have different structural and amino acid preferences - Molecular BioSystems (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C4MB00425F

Dissecting the role of low-complexity regions in the evolution of vertebrate proteins | BMC Ecology and Evolution | Full Text

Phosphorylation of the FUS low‐complexity domain disrupts phase separation, aggregation, and toxicity | The EMBO Journal
Phase Separation by Low Complexity Domains Promotes Stress Granule Assembly and Drives Pathological Fibrillization

Dynamic arrest and aging of biomolecular condensates are modulated by low-complexity domains, RNA and biochemical activity | Nature Communications
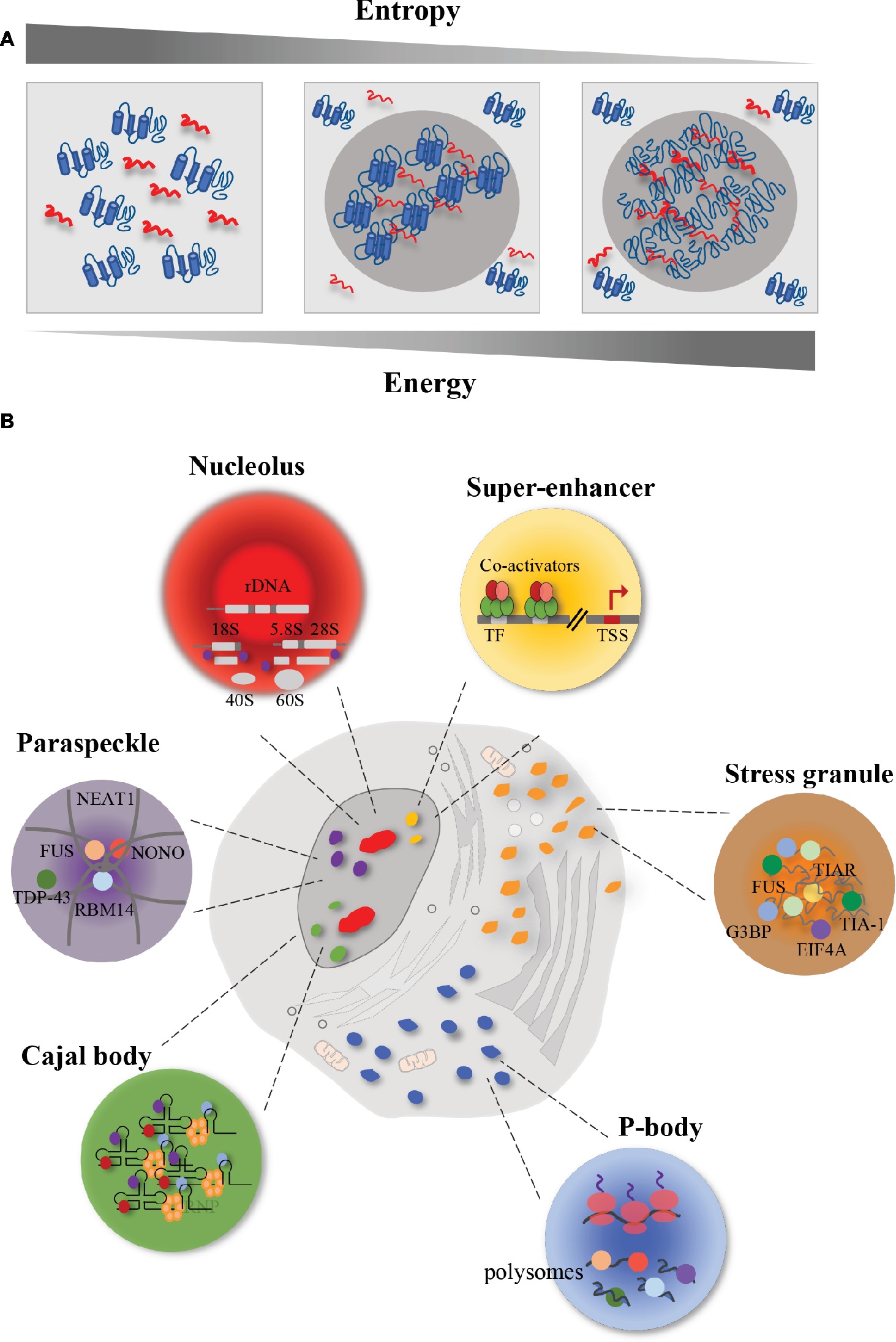
Frontiers | Aberrant Phase Transitions: Side Effects and Novel Therapeutic Strategies in Human Disease
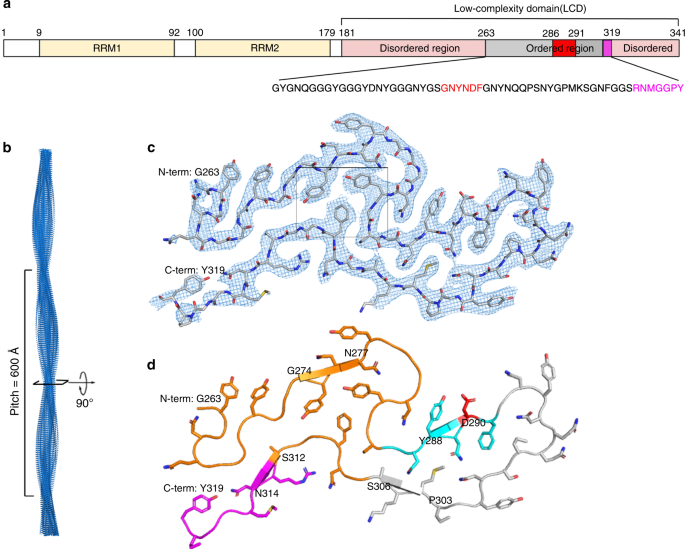
CryoEM structure of the low-complexity domain of hnRNPA2 and its conversion to pathogenic amyloid | Nature Communications
Phase separation of low-complexity domains in cellular function and disease | Experimental & Molecular Medicine

Shasha Chong on Twitter: "(3/4) We also provide proof-of-concept demonstration that single-molecule measurements of protein diffusion rates can serve as an effective means for detecting phase separation in vivo. We detected a



